CSA Examples
CSA 1
Patient with traumatic brain injury who is sedated and paralysed. Sudden spike in ICP associated with tachycardia, hypertension and dilated pupils – click for answer
CSA 2
A patient with meningitis and cerebral oedema has cerebral monitoring applied on admission to PICU. They are intubated and sedated with morphine/midazolam. Initially the EEG is relatively flat with delta waves (SEF 3.5 – 4Hz).

Over the next hour there are frequent spikes of higher frequency activity with values for SEF increasing to a high as 18Hz. These spikes are unresponsive to boluses of midazolam. The CSA tracing demonstrating the spikes and the raw EEG captured during one of the spikes in high frequency activity is displayed below.

What is the cause of these high frequency spikes – click for answer
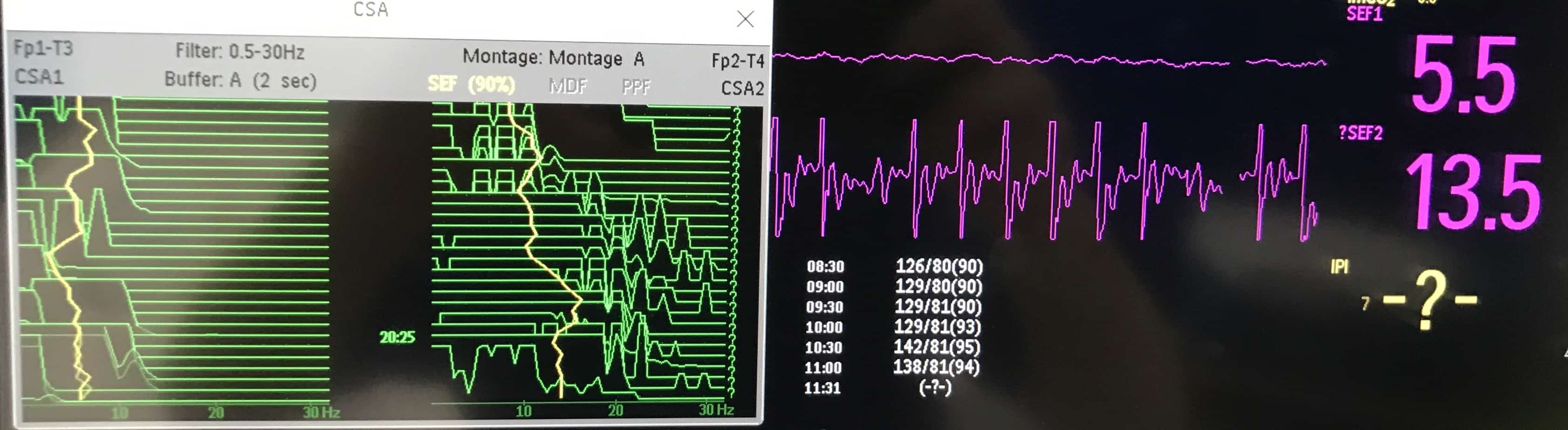
CSA 3
A patient with refractory status epilepticus is commenced on a thiopentone infusion in PICU with the aim of achieving burst suppression. Has the patient stopped seizing? Has burst suppression been obtained? – click for answer
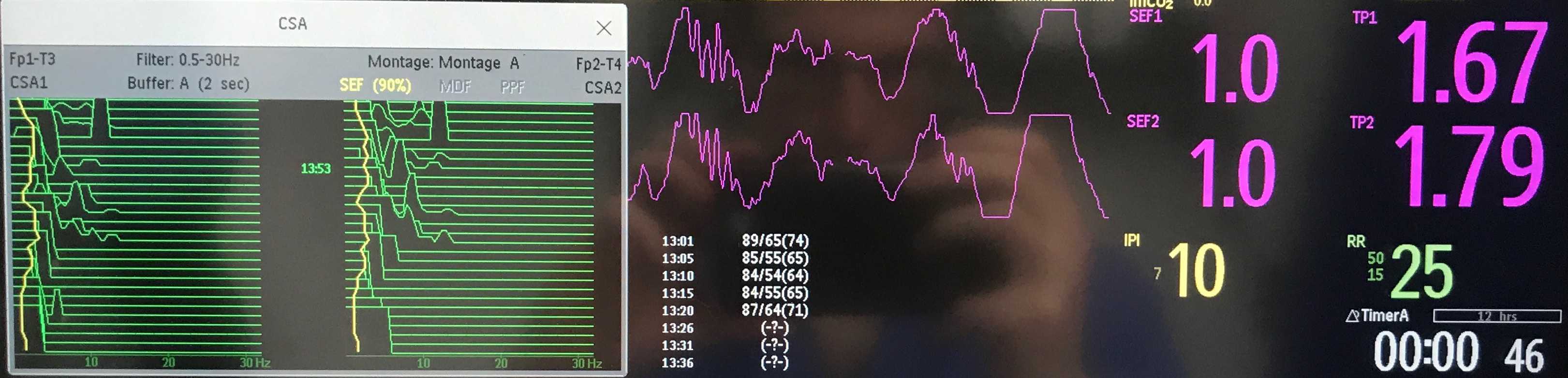
CSA 4
A patient with meningitis has cerebral monitoring applied on admission to PICU. They are intubated and sedated with morphine/midazolam. Initially the EEG is relatively flat with delta waves (SEF 3 – 3.5Hz).

The patient develops cycling movements of their right arm and leg associated with a sudden change in the CSA.
What is the cause for thIs? – click for answer
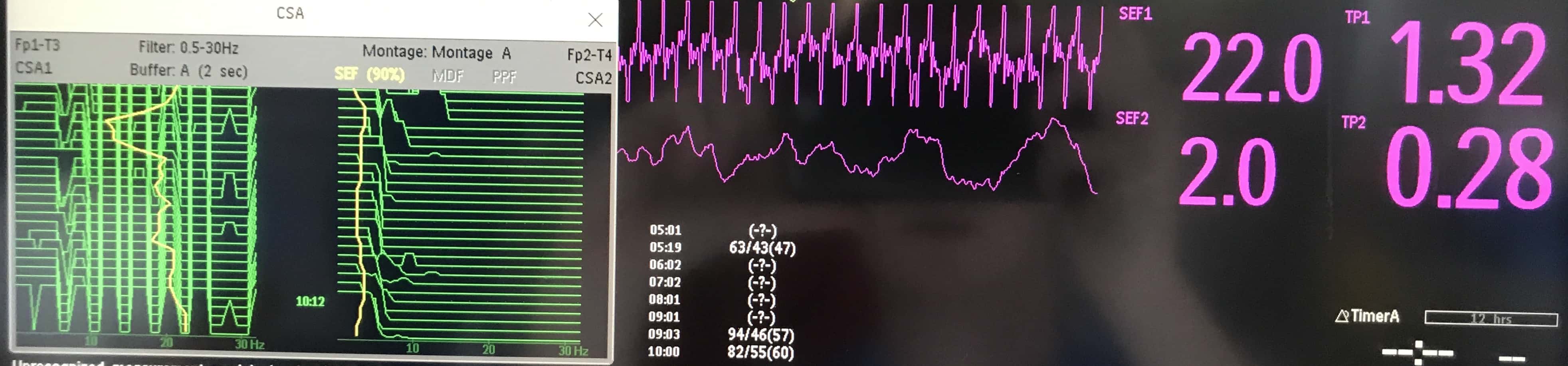
CSA 5
A patient is admitted to PICU following a prolonged cardiac arrest. They undergo standard neuroprotective measures including active normothermia, deep sedation (morphine and midazolam) and are paralysed. Cerebral monitoring is applied due to risk of nonconvulsive status epilepticus.
Although there are no clinical signs of seizure activity (absence of tachycardia, hypertension and pupils are pin point) concerns are raised about the possibility of seizure activity on the CSA due to persistent bilateral high frequency activity (SEF = 24Hz). TP is 0.5 (not shown on image).

A bolus of thiopentone is administered which causes flattening of the CSA for a few minutes before the high frequency activity returns and the CSA looks identical to before the thiopentone bolus.
What is the cause of these high frequency spikes – click for answer
CSA 6
A patient is admitted to PICU following a prolonged cardiac arrest. They undergo standard neuroprotective measures including active normothermia, deep sedation (morphine and midazolam) and are paralysed. Cerebral monitoring is applied due to risk of nonconvulsive status epilepticus.

What does the CSA show – click for answer
![]()
